
The Average Costing Method, also known as the weighted average cost method, is a popular inventory valuation technique. It calculates the cost of inventory items by averaging the total cost of goods available for sale over a specific period and dividing it by the total number of units available for sale. This method is particularly useful for businesses with large volumes of similar inventory items, as it simplifies the process of assigning costs to inventory and COGS. This method assumes that all units of inventory are identical and interchangeable, regardless of when they were purchased or at what cost. It is particularly useful for businesses with large quantities of similar or identical inventory items, as it simplifies the accounting process. The average cost method utilizes the average of every similar good in the inventory irrespective of the date of purchase.
How Will You Determine Your Average Inventory Cost?
Finally, this quantity is multiplied by weighted average cost per unit to give an estimate of ending inventory cost. The cost of goods sold valuation is the amount of goods sold times the weighted average cost per unit. The sum of these two amounts (less a rounding error) equals the total actual cost of all purchases and beginning inventory. For example, businesses that adopt average cost method need to continue to use this method for future accounting periods.
The average cost calculation formula is as follows:
When integrating the average cost method into inventory strategies, it’s important to consider the impact on pricing strategies and inventory turnover. Since the method provides a consistent cost figure, businesses can set prices with a clear understanding of their margins. The average cost method is a widely recognized technique for inventory valuation, essential in the financial reporting and tax calculation of businesses that hold inventory. Its significance lies in its impact on the cost of goods sold (COGS) and ultimately on net income and tax liability.
A Summarized Guide to Inventory Costing Methodologies
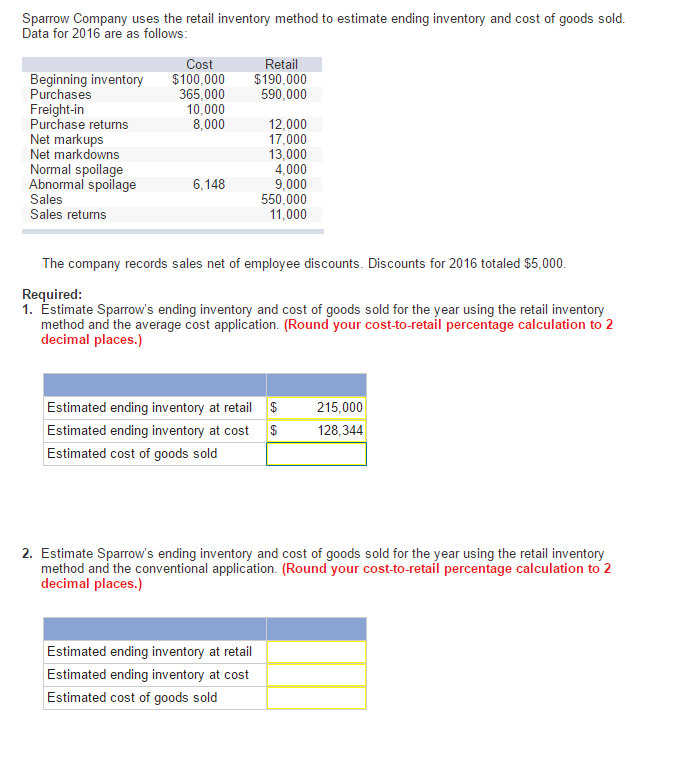
In the average cost method, we will assume that the unit sold and the ending inventory unit are both valued at the average cost of the two units, which is $6 [($5+$7) ÷ 2]. To explain the can i deduct private mortgage insurance basic principle of the average cost method, let’s assume there are just two identical inventory units. Any business that sells products must find an efficient way to deal with inventory.
Income Statement
This average cost is used to value the inventory sold and the remaining stock, providing consistent valuation. Calculating the ending inventory is essential in inventory costing and management. Calculating ending inventory and COGS under average cost method depends on the inventory system. U.S. GAAP allows for last in, first out (LIFO), first in, first out (FIFO), or average cost method of inventory valuation. On the other hand, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) do not allow LIFO because it does not typically represent the actual flow of inventory through a business.
Explore the benefits of the Average Cost Method for inventory valuation and how it can streamline your business’s financial strategies. This means that the cost of all 15 pairs is treated as if they were $11 each. On 2 January, more units costing $40 per unit are added to the inventory. Now that we know there are 75 units of ending inventory, we can calculate the ending inventory value using the formula below.
- It calculates the cost of ending an inventory against the cost of the goods sold in a particular period based on the weighted average cost per unit of inventory.
- FIFO offers a company financial reporting that reflects their industry’s current market conditions and is often the choice of a manufacturer dealing with perishable goods.
- The Average Cost Method is an inventory valuation technique used in accounting and finance to calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the value of ending inventory.
The simple average unit cost of 6.33 compares to the weighted average cost calculate earlier of 6.20. The method gives a reasonable estimate of the inventory value when the beginning inventory and purchases are of a similar level. The cost of goods sold is crucial to you, investors, your business, and analysts. It is derived from the sales revenue to determine the gross margin on the income statement. Your business and other businesses can use the average cost inventory or the other two methods (FIFO and LIFO) to ascertain the cost of goods sold. Assume that both beginning inventory and beginning inventory cost are known.
It is the easiest to calculate because it tells you the specific source of purchase inventory. If a car dealership buys a vehicle at $20000 and sells it at $70000, they will want to show the exact cost of the sold car as opposed to another car. In other words, using unique identification helps you to match the inventory costs and the revenue generated.
As prices rise, the average cost will typically be lower than the most recent purchase price, leading to a lower COGS on the income statement and a potentially higher gross profit margin. This can be particularly appealing to businesses looking to manage their income statements prudently during volatile economic conditions. The average cost method finds varied applications across different industries, each with its own considerations. In sectors like manufacturing, where products are produced in large batches, this method provides a streamlined approach to inventory costing. It ensures that manufacturing entities can maintain consistent cost records without tracking individual component costs.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), making it a versatile choice for multinational companies. For example, if a company buys 100 units at $10 each and another 100 units at $15 each, the total cost of goods available for sale would be $2,500. Dividing this by 200 units results in an average cost of $12.50 per unit.