Using the indirect method, actual cash inflows and outflows do not have to be known. The indirect method begins with net income or loss from the income statement, then modifies the figure using balance sheet account increases and decreases, to compute implicit cash inflows and outflows. The statement of cash flows, also called the cash flow statement, is the fourth general-purpose financial statement and summarizes how changes in balance sheet accounts affect the cash account during the accounting period. It also reconciles beginning and ending cash and cash equivalents account balances. Under IFRS, there are two allowable ways of presenting interest expense or income in the cash flow statement. Many companies present both the interest received and interest paid as operating cash flows.
2.5 Comparative Operating Activities Sections – Statement of Cash Flows
As of September 30, 2024, the Company had $5,221.8 million of total debt and $4,790.1 million of Net Debt. The terms of our capital structure include no material maintenance covenants, and there are no material debt maturities prior to May 2026. In January 2016 IAS 7 was amended by Disclosure Initiative (Amendments to IAS 7). These amendments require entities to provide disclosures about changes in liabilities arising from financing activities.
What Does a Negative Cash Flow From Financing Mean?
The starting cash balance is necessary when leveraging the indirect method of calculating cash flow from operating activities. Any information that relates to interest earned on an interest-bearing account or the amount of income taxes paid in a reporting period is classified under a supplemental section at the end of the cash flow statement. This section is also used to record any significant exchanges that did not involve a cash transaction, such as exchanging stock. Small businesses may not record stock, but if you use an interest-bearing business bank account, you should report that information here. Each of the three sections is summarized by one number, which is the net cash flows amount. If the summary number is positive, it means that more cash was received than was paid out for that activity during the accounting period.
The three sections of a cash flow statement

In other words, the financing section on the statement represents the amount of cash collected from issuing stock or taking out loans and the amount of cash disbursed to pay dividends and long-term debt. You can think of financing activities as the ways a company finances its operations either through long-term debt or equity financing. The cash flow statement will not present the net income of a company for the accounting period as it does not include non-cash items which are considered by the income statement. The CFS is one of the most important financial statements for a business.
- It’s important to note that cash flow is different from profit, which is why a cash flow statement is often interpreted together with other financial documents, such as a balance sheet and income statement.
- The cash flow statement reflects the actual amount of cash the company receives from its operations.
- But it still needs to be reconciled, since it affects your working capital.
- The indirect method begins with net income or loss from the income statement, then modifies the figure using balance sheet account increases and decreases, to compute implicit cash inflows and outflows.
- The terms of our capital structure include no material maintenance covenants, and there are no material debt maturities prior to May 2026.
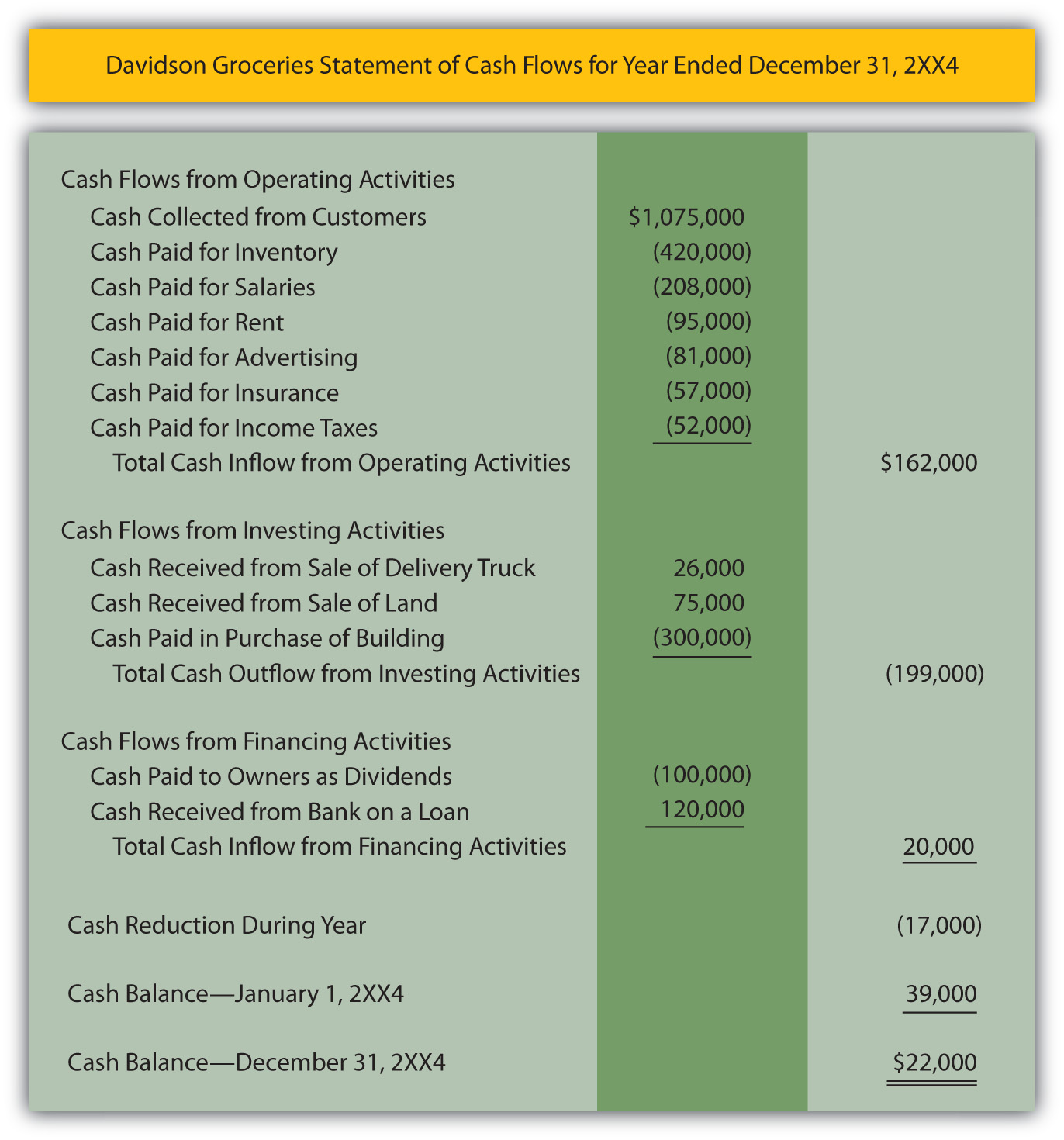
A positive net cash flow indicates a company had more cash flowing into it than out of it, while a negative net cash flow indicates it spent more than it earned. The first step in preparing a cash flow statement is determining the starting balance of cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the reporting period. This value can be found on the income statement of the same accounting period. The following section will show you how to prepare the statement of cash flows (direct method for operating activities section) on page 270 from the financial statements on page 255. The following is a sample statement of cash flows that has been prepared based on the financial statements presented on page 255.
The CFS is distinct from the income statement and the balance sheet because it does not include the amount of future incoming and outgoing cash that has been recorded as revenues and expenses. Therefore, cash is not the same as net income, which includes cash sales as well as sales made on credit on the income statements. Cash from financing activities includes the sources of cash from investors and banks, as well as the way cash is paid to shareholders. This includes any dividends, payments for stock repurchases, and repayment of debt principal (loans) that are made by the company. Investing activities include any sources and uses of cash from a company’s investments. Purchases or sales of assets, loans made to vendors or received from customers, or any payments related to mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are included in this category.
The business brought in $53.66 billion through its regular operating activities. Meanwhile, it spent approximately $33.77 billion in investment activities, and a further $16.3 billion in financing activities, for a total cash outflow of $50.1 billion. This section reports cash inflows what is form 8885 and outflows that stem directly from a company’s main business activities. These activities may include buying and selling inventory and supplies and paying employee salaries. Any other forms of inflows and outflows, such as investments, debts, and dividends, are not included.
When all three statements are built in Excel, we now have what we call a “Three-Statement Model”. The Company uses net leverage and Net Debt to evaluate the Company’s liquidity. We believe these measures are an important indicator of the Company’s ability to service its long-term debt obligations. In May 2023 the Board issued Supplier Finance Arrangements (Amendments to IAS 7 and IFRS 7) to require an entity to provide additional disclosures about its supplier finance arrangements.